ARC WELDING WITH COATED ELECTRODES
(M.M.A. Manual Metal Arc)
Arc welding with coated electrodes is a manual process where the heat source consists of the electric arc.
When the arc strikes between the coated electrode (by means of an electrode holder clamp) and the piece to be welded (base material), it generates heat which causes rapid melting of both the base material and the electrode (weld material).
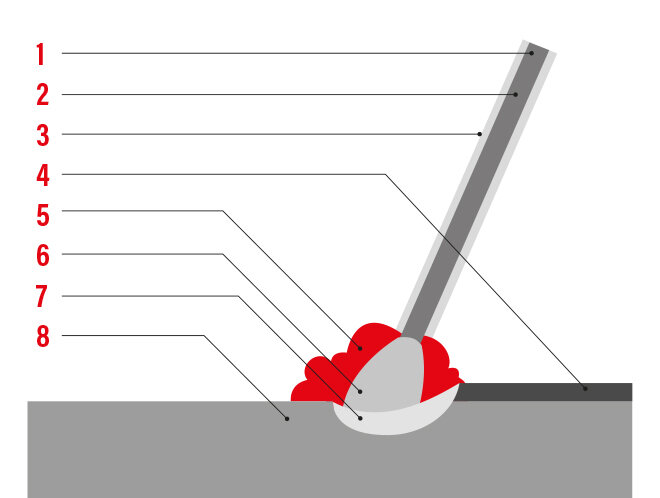
- Electrode
- Core
- Coating
- Slag
- Gaseous protection
- Welding arc
- Melting pool
- Base material

The welding circuit consists essentially of the following elements:
- POWER SOURCE
- ELECTRODE HOLDER CLAMP
- EARTH CLAMP
- COATED ELECTRODE
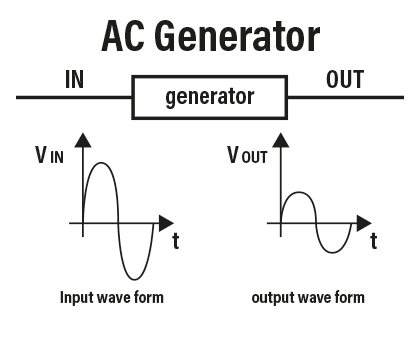
ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC) POWER SOURCE
The power source output current takes the form of a sine wave, which changes its polarity at regular intervals, with a frequency of 50 or 60 cycles per second (Hertz). It is obtained using a transformer, which converts the mains current into a suitable current for welding. This is for electromechanical welding machines.
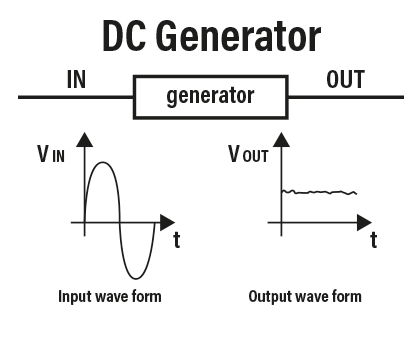
DIRECT CURRENT (DC) POWER SOURCE
The power source output current has a continuous wave form, which is obtained by means of a device, the rectifier, which is situated at the base of the transformer and can convert from alternating to direct current. This output is typical of electronic SCR and inverter power sources.
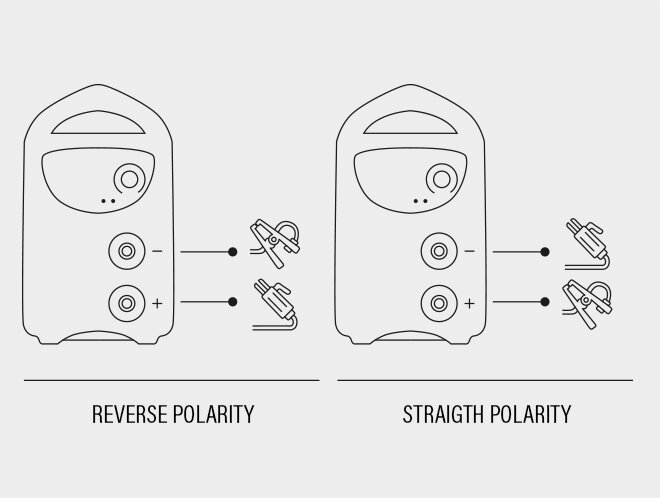
If the welding circuit has a direct current (DC) power source, it can be further classified according to the method of connecting the power source poles to the material to be welded:
- Straight polarity connection
Straight polarity connection occurs when the clamp cable (with the electrode holder clamp) is connected to the negative pole (-) of the power source and the earth cable (with the earth clamp) to the positive pole (+) of the power source. The electric arc concentrates the heat produced on the piece and causes its melting. In this way, as the core of the electrode melts, it is deposited and penetrates into the welding joint.
- Reverse polarity connection
Reverse polarity connection occurs when the clamp cable (with the electrode holder clamp) is connected to the positive pole (+) of the power source and the earth cable (with the earth clamp) to the negative pole (-) of the power source. The heat of the electric arc is mostly concentrated at the tip of the electrode.Each type of electrode requires a specific current type (AC or DC) and, in the case of DC current, a specific polarity: the choice of the electrode therefore depends on the type of power source used. Incorrect use will cause arc stability problems and hence also welding quality problems.


 The primary function of the electrode holder clamp is to support the electrode, guaranteeing a good electrical contact for current passage; it should also guarantee sufficient electrical insulation for the welding operator.
The primary function of the electrode holder clamp is to support the electrode, guaranteeing a good electrical contact for current passage; it should also guarantee sufficient electrical insulation for the welding operator. The earth clamp is a tool that, via the earth cable, ensures the electrical circuit to be closed between the welding power source and the piece to be welded. The clamp and earth cables, connected to the electrode holder clamp and earth clamp respectively, permit an electrical connection between the power source and the base material to be welded. The choice of cable section and length should be based on the maximum welding current in amps.
The earth clamp is a tool that, via the earth cable, ensures the electrical circuit to be closed between the welding power source and the piece to be welded. The clamp and earth cables, connected to the electrode holder clamp and earth clamp respectively, permit an electrical connection between the power source and the base material to be welded. The choice of cable section and length should be based on the maximum welding current in amps. The coated electrode consists of a core and a coating which have different but complementary functions: the core acts mainly as a conductor for the arc power supply and as supplier of the material that fills the joint; the coating, on the other hand, has the main function to protect the weld pool and stabilise the arc.
The coated electrode consists of a core and a coating which have different but complementary functions: the core acts mainly as a conductor for the arc power supply and as supplier of the material that fills the joint; the coating, on the other hand, has the main function to protect the weld pool and stabilise the arc.